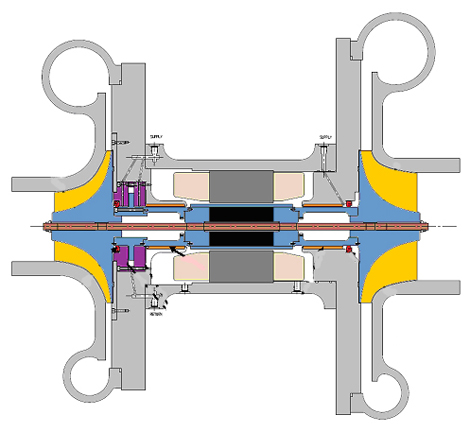
Barber-Nichols Inc. (BNI) is pleased to be selected by NASA for a Phase II Small Business Innovative Research (SBIR) award to develop a new high-speed, two-stage compressor for launch vehicle propellant densification.

Many of today’s large launch vehicles utilize liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen as engine propellants and densified propellants are desirable for three reasons. First, when propellants are subcooled and densified their volumes decrease by 7-15%. As a result, smaller, lighter propellant tanks can be used. Second, densified propellants have lower pressure so propellant tank walls can be thinner and lighter. And finally, densified propellants have a higher available Net Positive Suction Head (NPSH) which allows launch vehicle designers to utilize smaller, lighter turbopumps because they can operate at higher speeds without cavitating. Because it costs about $10,000 USD per pound to place a launch vehicle into low earth orbit, propellant densification results in substantial cost savings and the ability to launch greater payloads.
The new high-speed, two-stage compressor being developed under this SBIR aims to further reduce costs and simplify the machinery required to densify propellants by replacing traditional grease-packed ball bearings with advanced foil bearings designed to operate in a cryogenic hydrogen environment. Due to reasons described in BNI’s Guidelines for Determining Foil Bearing Applicability white paper, foil bearings have an extremely long life and will make it possible for this compressor to operate at much higher speeds (35,000 rpm) and essentially accomplish what previously required four separate compressors.
Barber-Nichols has 40 years of experience with pumps, compressors, and systems for cryogenic fluids. In 1974, BNI designed and built its first cryogenic pump for the National Bureau of Standards (now the National Institute of Standards and Technology). The liquid helium pump exceeded NIST’s expectations and since that time BNI’s reputation as an international manufacturer of custom cryogenic circulators, compressors, and pumps has flourished. BNI’s cryogenic machinery is hermetically sealed and minimizes heat leak which are both crucial for cryogenic applications and is currently being used around the world for:
- The circulation of argon (87 K [-303 °F]) for particle research.
- The circulation of nitrogen (77 K [-321 °F]) for the cooling of high-temperature superconducting magnets & synchrotron beamline crystals.
- The circulation of supercritical helium (4.2 K [-452 °F]) for the cooling of superconducting magnets.
- The circulation of liquid neon, krypton, xenon, and more.